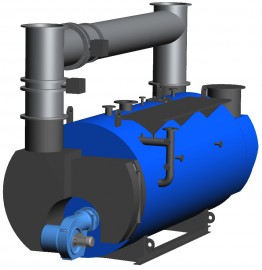
COMBINED BOILERS
COMBINED BOILERS
PB-(X)-K
Three-pass medium-pressure boilers combusting gaseous and liquid fuels with an autonomous flue gas pass for heat
recuperation
In compliance with the requirements of standard ČSN EN 12 953 and directive EC 97/23
Design
The boiler body consists of a cylindrical shell and two reinforced bottoms. It is divided into a burner and flue gas parts.
The burner part consists of an asymmetrically bedded boiler flue, a water cooled inflective chamber and a nest of stay tubes of the second and third pass. The front inflective chamber is not cooled. It is closed with a door enabling cleaning of the generating surfaces. Boiler venting is provided by a flue gas collector in the rear part of the boiler. Flue gas discharge is realized via a chimney neck with an upper or rear outlet.
The flue gas pass consists of a nest of stay tubes - the number of stay tubes nests is in accordance with the number of connected sources and their parameters. The front part of the boiler includes a flue gas chamber with a flue gas inlet; the rear part of the boiler includes a flue gas chamber with an upper or a rear flue gas outlet.
Working principle
The flue gas part of the boiler can be used to increase the operation efficiency for existing energy sources, e.g. cogeneration unit, flue gas turbine, waste flue gas from biomass combustion, etc.
The boiler can be operated in both a mode with a concurrent operation of both parts, i.e. burner and flue gas, and also in a mode with an autonomous operation of one of them.
Efficiency
The heat contained in flue gasses leaving the conventional part of the boiler can be transferred to feed water in the exhaust-heat exchanger. Energy thus gained increases the boiler efficiency of up to 5% reducing thus the fuel consumption.
Economizer
It supplements the basic design of the boilers. It can be integrated into the flue gas collector or autonomously placed at the flue gas outlet.
The economizer provides a highly efficient heat transfer - the counter-flow principle. It consists of nests of finned or plain tubes in the flue gas channel with admission in the water chambers.
Flue gas bypass
The boiler can be added with a flue gas bypass fitted with a couple of flue gas flaps for continuous operation of the primary flue gas source without the boiler being necessary to operate or as an emergency safety element.
Maintenance
A manhole together with inspection holes enables the boiler inner inspection. The generating surfaces are easily accessible for cleaning guaranteeing thus a permanently high efficiency.
Versions
The PB-(X)-K boilers can be supplied in steam, hot-water or warm-water versions.
BASIC TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
- Steam output 1 000 ÷ 16 000 kg/h
- Heat output 1 ÷ 10 MW
- Operation overpressure 6 ÷ 25 bar(g)
- Heat transfer media - steam, warm or hot water
- In compliance with technical requirements ČSN EN 12953
FUEL
- Natural gas
- Propane, propane-butane
- Low calorific power gasses - biogas
- Oil fuels
HEAT SOURCES
- Cogeneration units
- Flue-gas turbines
- Biomass combustion
- Process gas
ADVANTAGES
- High lifetime
- Increase of heat production process efficiency or increase of the combustion process efficiency
- Use of different heat sources
- Large-capacity boiler
- Combustion of different types of fuel
- Design customization
- High-quality warranty and post-warranty service
- Boilers in connection with low-emission burners meet the legal emission limits for gaseous and liquid fuels
BASIC CONNECTION DIAGRAM OF A COMBINED BOILER - STEAM VERSION
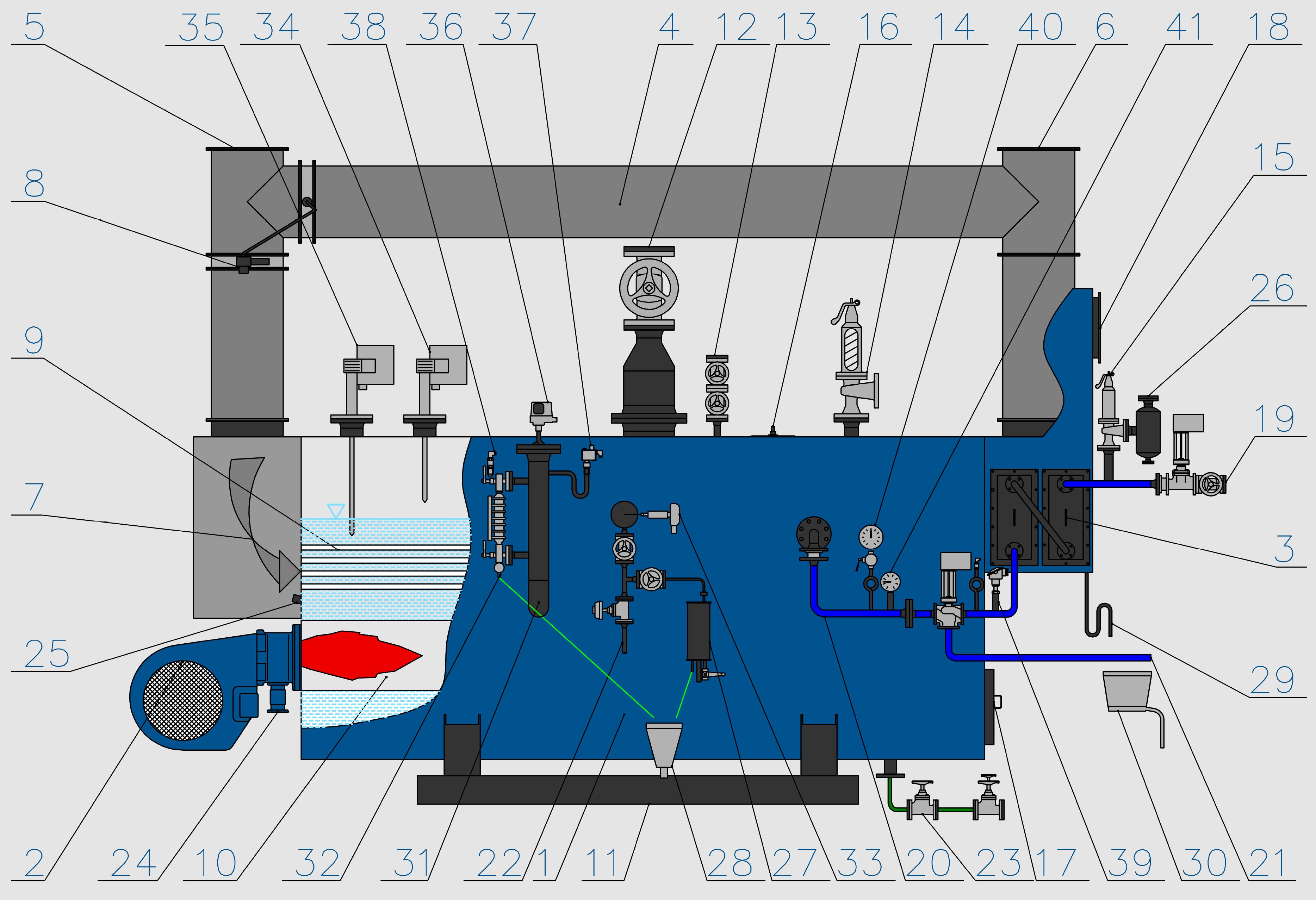
1) Boiler
2) Burner
3) Economizer
4) Flue gas bypass
5) Flue gas inlet
6) Flue gas outlet
7) Flue gas
8) Flue gas flap
9) Utilization part
10) Boiler flue
11) Base
12) Saturated steam outlet
13) Deaeration
14) Boiler relief valve
15) Economizer relief valve
16) Manhole into the boiler
17) Manhole into the combustion chamber
18) Flue gas outlet from the conventional part
19) Feeding branch before the economizer
20) Feeding branch before the boiler
21) Bypass into the feeding tank
22) Boiler continual blown-down
23) Boiler periodical blown-down
24) Fuel feed
25) Sight glass into the flue
26) Blow-off damper
27) Sample cooler
28) Non-pressure waste sunk basin
29) Condensing loop
30) Neutralization box
31) Column with level measurement
32) Water-level gauge
33) Conductivity probe
34) Water level regulation
35) Water level monitoring
36) Emergency manostat
37) Operation manostat
38) Pressure sensor
39) Temperature sensor
40) Manometer
41) Thermometer